Understanding EC2 Instance Purchasing Options: A Complete Guide
Amazon EC2 offers loads of purchasing options tailored to different workloads, pricing and needs. Choosing the right purchasing option can significantly optimize your cloud costs
Understanding EC2 Instance Purchasing Options: A Complete Guide
Amazon EC2 offers a variety of purchasing options tailored to different workloads, pricing needs, and commitment levels. Choosing the right purchasing option can significantly optimize your cloud costs while ensuring performance and reliability.
Real-World Examples to Relate To
Before diving into the details, let’s look at some real-world examples that junior developers might encounter:
You’re building a personal portfolio website – You don’t need it running 24/7, so an On-Demand Instance makes sense.
Your company has a SaaS product with stable daily traffic – Using Reserved Instances can save costs in the long run.
You’re experimenting with AI/ML models – You need cheap, temporary resources, making Spot Instances a great option.
Your team needs a testing environment for a project – On-Demand or Spot Instances allow flexibility without commitment.
You work in a finance or healthcare company with strict compliance rules – A Dedicated Host ensures your instances are on isolated hardware.
Now, let’s break down these options in more detail:
1. On-Demand Instances
On-Demand Instances are ideal for short-term, unpredictable workloads where flexibility is crucial. With On-Demand pricing, you pay per second (Linux) or per hour (Windows) without any long-term commitment.
Use Cases:
Applications with variable traffic.
Development and testing environments.
Workloads that require high flexibility.
Pros:
No upfront cost.
Highly flexible with instant provisioning.
Cons:
Most expensive option if used continuously.
2. Reserved Instances (RI) (1 & 3 Years)
Reserved Instances are designed for long-term workloads with stable usage. By committing to a 1-year or 3-year term, you can save up to 75% compared to On-Demand pricing.
Use Cases:
Applications with consistent, predictable demand.
Enterprise workloads that run 24/7.
Pros:
Significant cost savings over On-Demand.
Capacity reservation ensures availability.
Cons:
Less flexibility; changing instance type may require Convertible RIs.
3. Convertible Reserved Instances
Convertible Reserved Instances function similarly to standard RIs but allow you to change instance families, OS, and tenancy while maintaining the discount.
Use Cases:
Businesses expecting changing workload requirements over time.
Long-term applications with evolving infrastructure needs.
Pros:
Offers flexibility in modifying instances.
Still provides cost savings.
Cons:
Slightly lower discounts than Standard Reserved Instances.
4. Savings Plans (1 & 3 Years)
Savings Plans offer a commitment-based pricing model where you agree to spend a fixed amount per hour in exchange for reduced pricing, without being tied to a specific instance type or family.
Use Cases:
Companies running diverse workloads across multiple instance types.
Organizations seeking long-term cost savings without rigid instance commitments.
Pros:
More flexibility than Reserved Instances.
Works across different instance families and AWS services.
Cons:
Requires commitment to a consistent spending level.
5. Spot Instances
Spot Instances allow you to access unused EC2 capacity at discounts of up to 90%. However, AWS can terminate Spot Instances anytime if it needs the capacity for On-Demand customers.
Use Cases:
Batch processing, data analytics, and rendering workloads.
Machine learning training jobs.
CI/CD workloads that can handle interruptions.
Pros:
Extremely cost-effective.
Ideal for fault-tolerant applications.
Cons:
Instances can be terminated unexpectedly.
6. Dedicated Hosts
Dedicated Hosts provide a physical EC2 server exclusively for your use, allowing full control over instance placement and compliance with licensing requirements.
Use Cases:
Organizations with strict compliance needs (e.g., finance, healthcare).
Businesses using Bring Your Own License (BYOL) for software like Windows or Oracle.
Pros:
Provides greater visibility and control over instances.
Meets strict regulatory and licensing requirements.
Cons:
Higher cost compared to other options.
7. Dedicated Instances
Dedicated Instances also run on hardware dedicated to a single customer but don’t provide control over instance placement like Dedicated Hosts do.
Use Cases:
Organizations with compliance needs but don’t require full server control.
Applications requiring isolated hardware for security reasons.
Pros:
Ensures no other customers share your hardware.
Simpler to set up than Dedicated Hosts.
Cons:
No control over server placement.
8. Capacity Reservations
Capacity Reservations allow you to reserve instance capacity in a specific AWS Availability Zone (AZ) without committing to long-term pricing like Reserved Instances.
Use Cases:
Mission-critical applications needing guaranteed availability.
Workloads requiring reserved capacity for seasonal spikes.
Pros:
Guarantees resource availability.
No long-term commitment required.
Cons:
No cost savings compared to On-Demand pricing.
Choosing the Right EC2 Instance Option
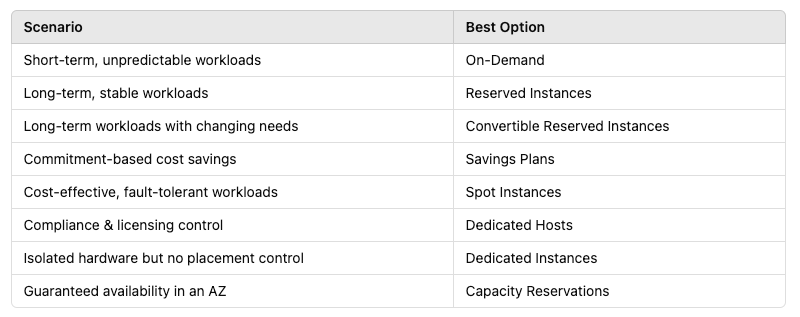
To summarize, here’s how to choose the best option based on your needs:
Conclusion
AWS EC2 offers multiple purchasing options, each tailored to different workload types and pricing preferences. Whether you need flexibility, cost savings, or compliance controls, choosing the right instance type can help optimize your AWS infrastructure efficiently.
Are you currently using EC2? Which pricing model works best for your workload? Let me know in the comments!